MSc Bioinformatics
Biocomputing II - Project work
The aim of the project is to expose you to a reasonably large collaborative programming project.
You will create a simple genome browser to look at genes in a given human chromosome. You will need to load the Genbank sequence data into a database and provide a web front end that allows you to view and query the data. You will also provide the ability to identify restriction enzyme cut sites within the DNA.
Your group will have been allocated a chromosome to work on, so your first task will be to download the human genomic DNA records (from the Download page) which contain coding sequences from Genbank for that chromosome onto your account on Pandora.
Your tasks are as follows:
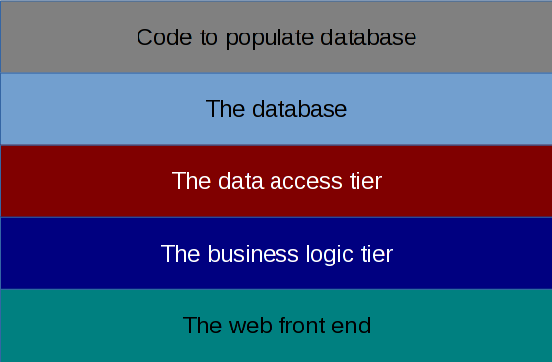
- Create a database tier:
- Design a relational database in which you will store appropriate pieces of data from the Genbank file. What data are appropriate will be up to you to decide given the other requirements of the project.
- Write a parser that can extract the relevant data from the Genbank file and convert the data to SQL that can be loaded into the database. Note that your parser will have to deal with identifying intron/exon boundaries and finding the coding sequence of the DNA (see notes below).
- The database tier also needs to provide a 'data access tier' - Python wrappers to the SQL that return the data required by the middle tier - i.e. an abstraction of the database design that returns the data requested.
- Create a middle layer / tier:
- The logic tier contains the "business rules" that take requests from the interface, extract data from the data tier, perform any needed processing of the data, including any calculations that need to be done. Note that the logic tier will not provide any information on how the results should be presented.
- Tasks for this tier include: identifying where the coding regions are and generating the coding DNA sequence; aligning the protein translation with the DNA coding sequence; identifying restriction enzyme (RE) sites; providing a list of known REs to the front end; identify whether an RE has restriction sites within the coding region; counting codon usage in a gene; calculating codon usage across all coding regions; extracting information from the database layer (e.g. the complete gene list or individual gene information)
- Web-based graphical user interface (front-end tier):
- A (set of) web pages that allow the user to query the database - via the middle tier.
- Supporting Python/CGI scripts that access the business logic layer of code when forms are submitted and generate new pages.
- Requirements for the queries are listed below.
All code must be commented internally and must be documented in a separate manual which will explain what each piece of code does. In particular, the middle layer code must be carefully documented to explain how each routine can be called from the graphical front end.
You should download some general guidance on what is expected. See the Good Code section for further help.